#!pip install ANNarchySynaptic transmission
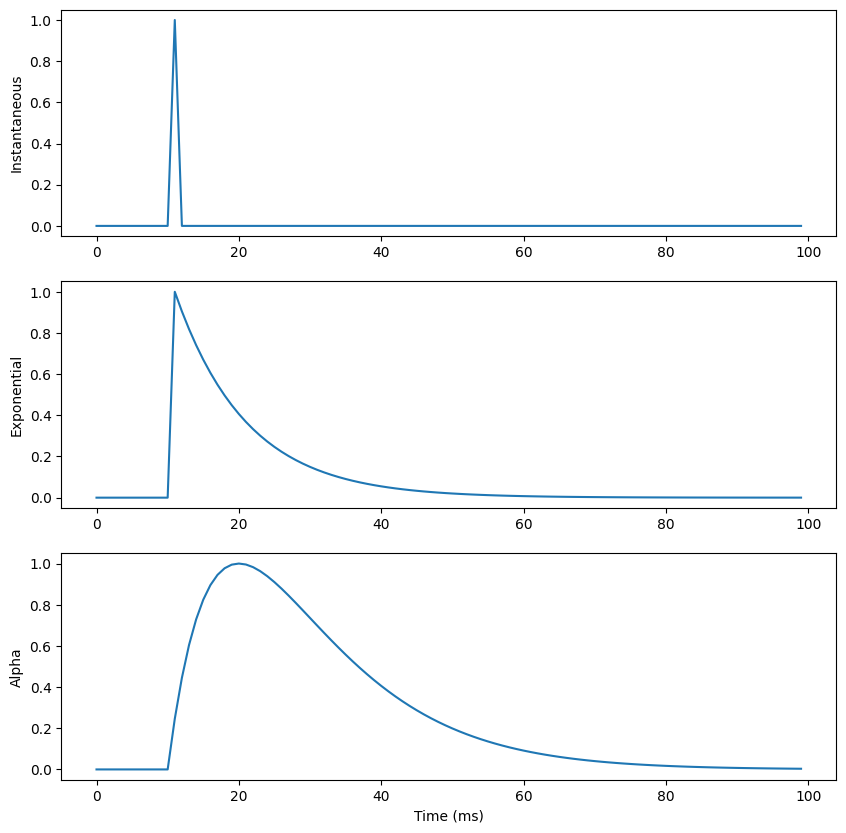
This notebook simply demonstrates the three main type of synaptic transmission for spiking neurons:
- Instantaneous
- Exponentially-decreasing
- Alpha-shaped
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import ANNarchy as annANNarchy 5.0 (5.0.0) on linux (posix).We use here a simple LIF neuron receving three types of projections (a, b, c). The conductance g_a uses instantaneous transmission, as it is reset to 0 after each step. g_b decreases exponentially with time following a first order ODE. g_c is integrated twice in alpha_c, leading to the alpha shape.
All methods use the exponential numerical method, as they are first order linear ODEs and can be solved exactly.
LIF = ann.Neuron(
parameters = dict(
tau = 20.,
E_L = -70.,
v_T = 0.,
v_r = -58.,
tau_b = 10.0,
tau_c = 10.0,
),
equations = [
# Membrane potential
ann.Variable('tau * dv/dt = (E_L - v) + g_a + g_b + alpha_c', init=-70.),
# Exponentially decreasing
ann.Variable('tau_b * dg_b/dt = -g_b', method='exponential'),
# Alpha-shaped
ann.Variable('tau_c * dg_c/dt = -g_c', method='exponential'),
ann.Variable('tau_c * dalpha_c/dt = exp((tau_c - dt/2.0)/tau_c) * g_c - alpha_c', method='exponential'),
],
spike="v >= v_T",
reset="v = v_r",
refractory = 2.0
)The LIF neuron will receive a single spike at t = 10 ms, using the SpikeSourceArray specific population.
net = ann.Network()
inp = net.create(ann.SpikeSourceArray([10.]))
pop = net.create(1, LIF)We implement three different projections between the same neurons, to highlight the three possible transmission mechanisms.
proj = net.connect(inp, pop, 'a')
proj.all_to_all(weights=1.0)
proj = net.connect(inp, pop, 'b')
proj.all_to_all(weights=1.0)
proj = net.connect(inp, pop, 'c')
proj.all_to_all(weights=1.0)<ANNarchy.core.Projection.Projection at 0x7f708bf066e0>net.compile()Compiling network 1... OK We monitor the three conductances:
m = net.monitor(pop, ['g_a', 'g_b', 'alpha_c'])inp.clear()
net.simulate(100.)data = m.get()plt.figure(figsize=(10, 10))
plt.subplot(311)
plt.plot(data['g_a'][:, 0])
plt.ylabel("Instantaneous")
plt.subplot(312)
plt.plot(data['g_b'][:, 0])
plt.ylabel("Exponential")
plt.subplot(313)
plt.plot(data['alpha_c'][:, 0])
plt.xlabel("Time (ms)")
plt.ylabel("Alpha")
plt.show()