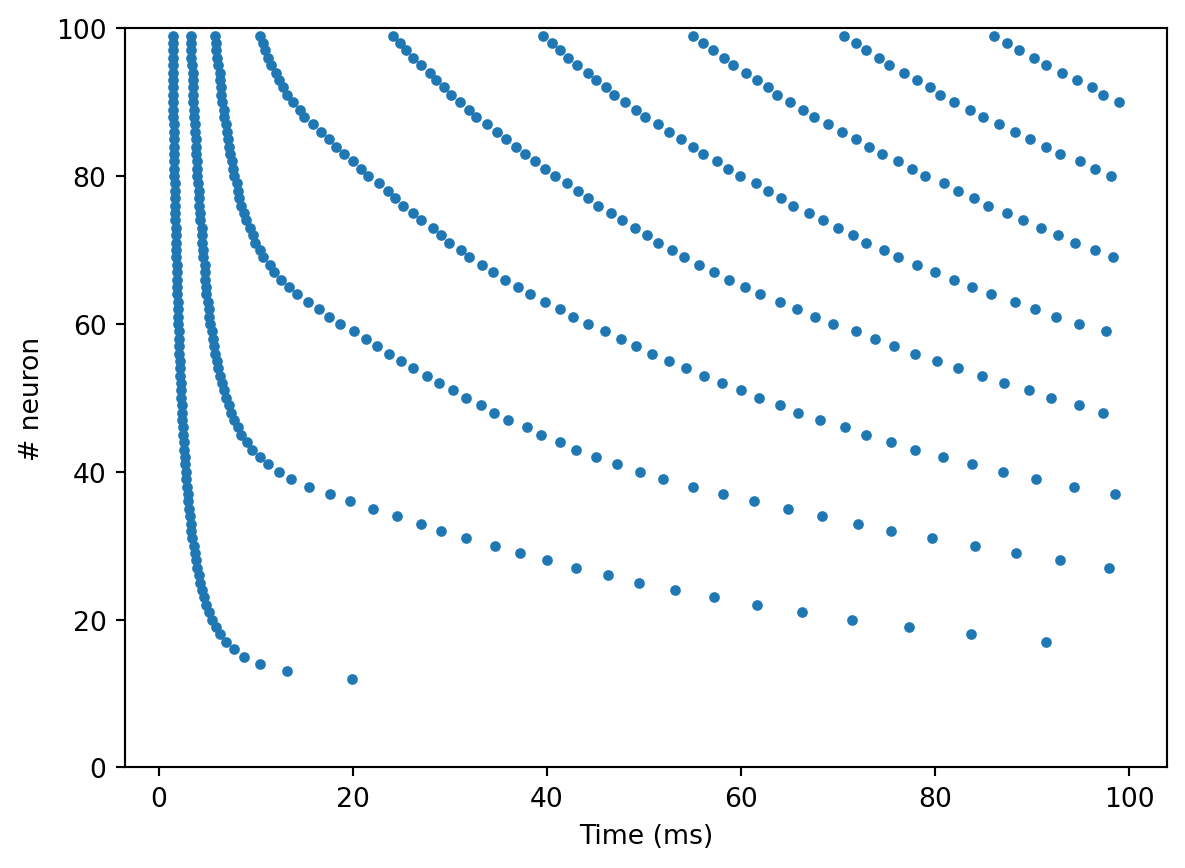
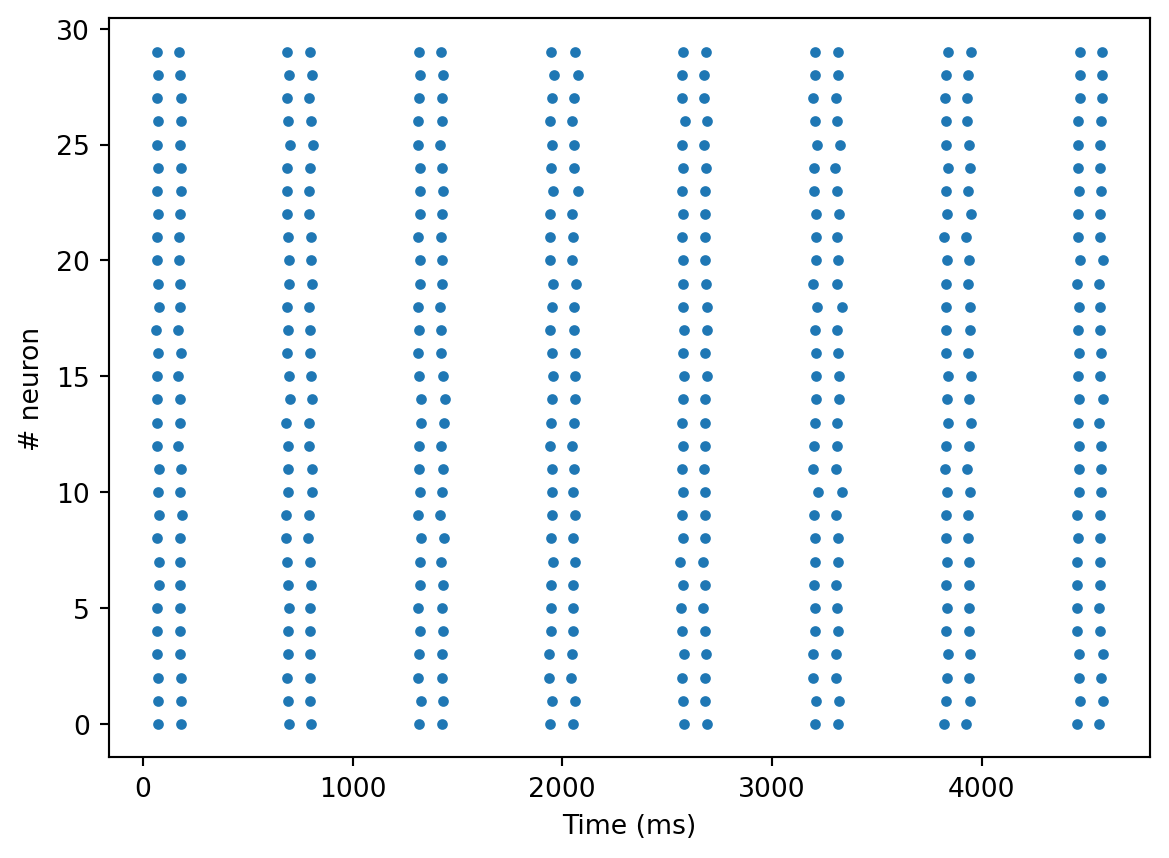
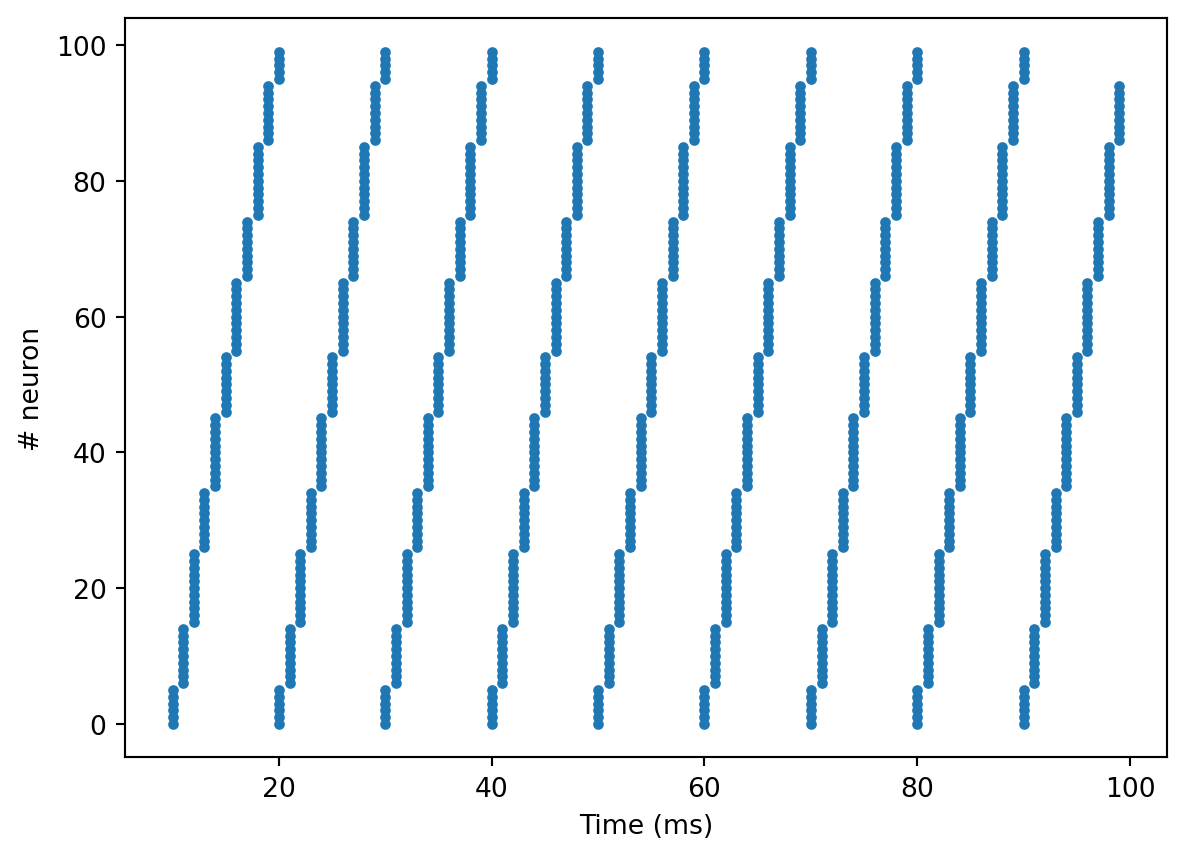
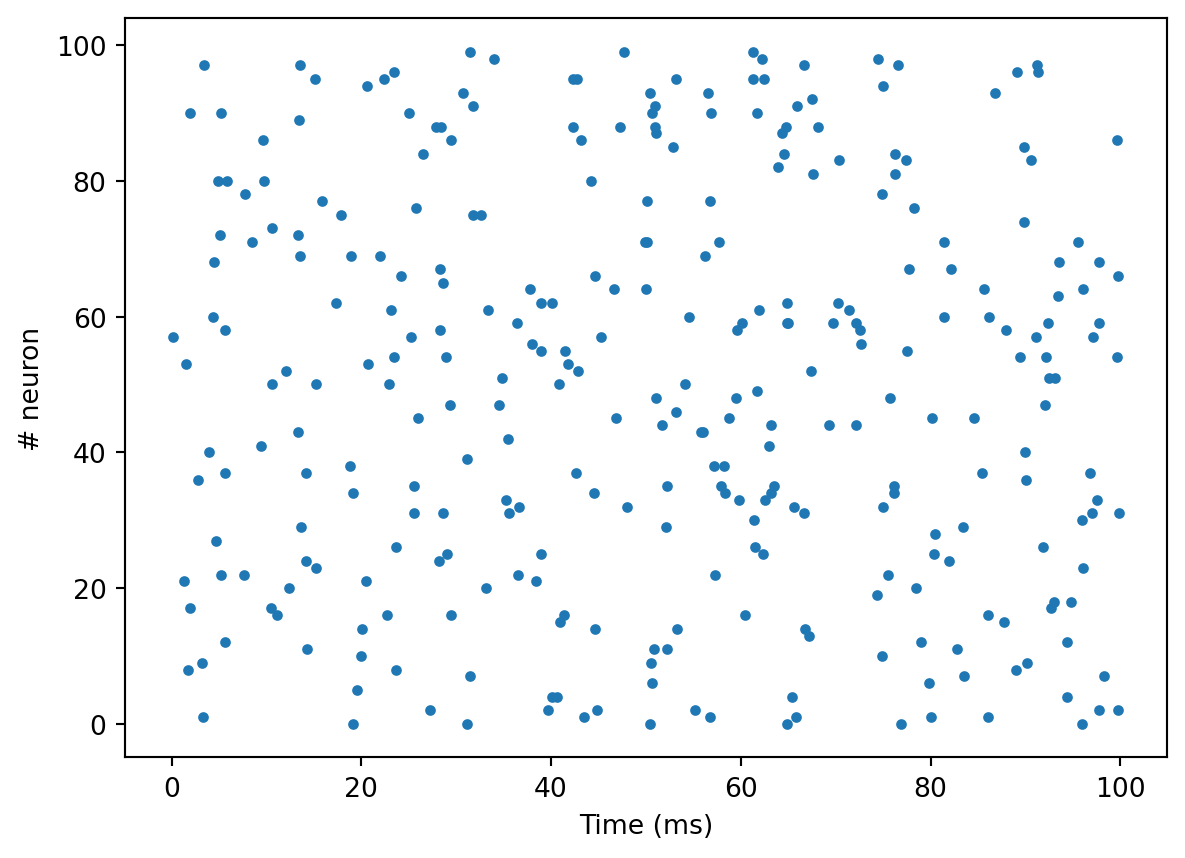
inputs = np.array(
[
[1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0],
[0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1]
]
)
# Network
net = ann.Network()
# Input
inp = net.create(ann.TimedArray(rates=inputs))
# Population
pop = net.create(10, Neuron(equations="r=sum(exc)"))
# Projection
proj = net.connect(inp, pop, 'exc')
proj.one_to_one(1.0)
# Compile and simulate
net.compile()
net.simulate(10.)