ANNarchy (Artificial Neural Networks architect)
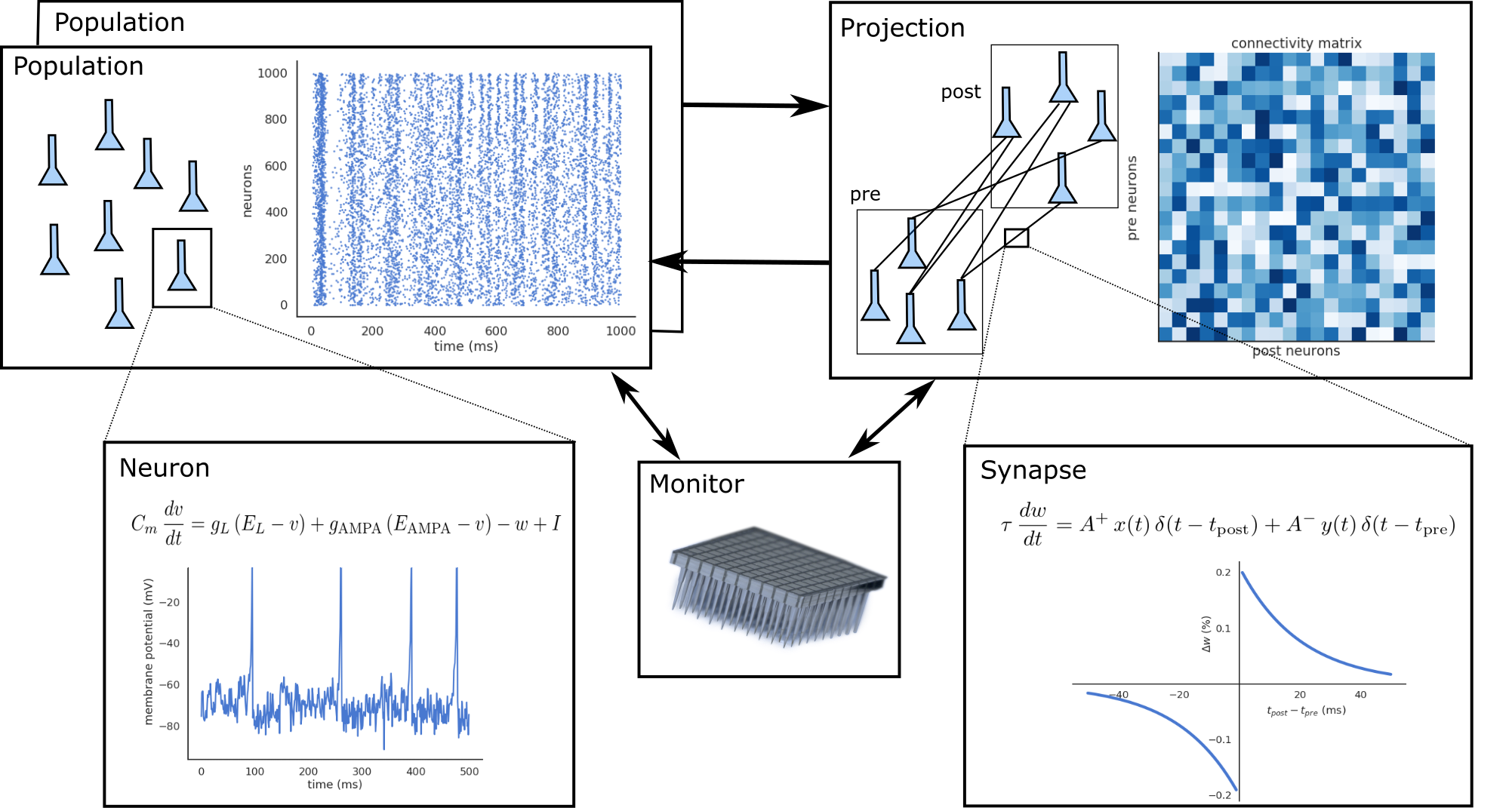
ANNarchy (Artificial Neural Networks architect) is a Python neurosimulator designed for rate-coded and spiking neural networks, released under the GNU GPL v2 or later.
Resources
- Source code: github.com/ANNarchy/ANNarchy
- Documentation: annarchy.github.io
- Forum: Google Forum
- Bug reports and feature requests: Github Issues
Documentation
- Installation instructions.
- Tutorial for a quick presentation of the simulator.
- Manual with a full description of the functionalities.
- Notebooks showcasing many different networks.
- Reference implementation with all classes and functions.
Citation
If you use ANNarchy for your research, we would appreciate if you cite the following paper. See the full list of publications related to ANNarchy here.
Vitay J, Dinkelbach HÜ and Hamker FH (2015). ANNarchy: a code generation approach to neural simulations on parallel hardware. Frontiers in Neuroinformatics 9:19. doi:10.3389/fninf.2015.00019
@article{Vitay2015,
title = {{{ANNarchy}}: A Code Generation Approach to Neural Simulations on Parallel Hardware},
author = {Vitay, Julien and Dinkelbach, Helge {\"U}. and Hamker, Fred H.},
year = {2015},
journal = {Frontiers in Neuroinformatics},
volume = {9},
number = {19},
doi = {10.3389/fninf.2015.00019},
url = {https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fninf.2015.00019},
abstract = {Many modern neural simulators focus on the simulation of networks of spiking neurons on parallel hardware. Another important framework in computational neuroscience, rate-coded neural networks, is mostly difficult or impossible to implement using these simulators. We present here the ANNarchy (Artificial Neural Networks architect) neural simulator, which allows to easily define and simulate rate-coded and spiking networks, as well as combinations of both. The interface in Python has been designed to be close to the PyNN interface, while the definition of neuron and synapse models can be specified using an equation-oriented mathematical description similar to the Brian neural simulator. This information is used to generate C++ code that will efficiently perform the simulation on the chosen parallel hardware (multi-core system or graphical processing unit). Several numerical methods are available to transform ordinary differential equations into an efficient C++ code. We compare the parallel performance of the simulator to existing solutions.}
}